What Crawl Budget Is And Why It’s Essential For SEO
Crawl budget is the number of pages search engines crawl on your website within a specific timeframe. Search engines like Google determine crawl budget using two factors: crawl limit (server capacity) and crawl demand (content importance). When websites waste crawl budget on parameter URLs, duplicate content, or broken links, search engines cannot efficiently discover and index important pages. This directly reduces SEO performance and organic traffic potential. At Eclipse Marketing, we help businesses optimize their crawl budgets to maximize search engine visibility and drive better organic results.
Crawl budget optimization becomes critical for websites exceeding 10,000 pages, where inefficient crawling can leave valuable content undiscovered. Google allocates crawl budget based on website authority, page popularity, content freshness, and server performance. Websites sharing hosting resources face reduced crawl limits, while dedicated hosting improves crawl allocation significantly.
Key crawl budget waste factors include accessible parameter URLs, duplicate content pages, slow-loading pages, broken redirects, and poor internal linking structures. Website owners can monitor their crawl budget through Google Search Console under Crawl Stats, which shows daily crawling activity and helps identify optimization opportunities for better search engine visibility.

What Does Crawl Budget Actually Mean?
Crawl budget represents the total number of pages search engines will examine on your website. This examination happens within a predetermined timeframe that search engines control and manage carefully.
Why Search Engines Set Crawl Budgets for Every Website
Search engines cannot operate with unlimited resources available to them at any given time. They must carefully divide their scanning attention across millions of different websites worldwide every day. Therefore, they require an effective method to prioritize their crawling efforts across the internet systematically. Setting specific crawl budgets for each individual website helps them accomplish this important goal efficiently. This budget system ensures search engines can manage their resources while still discovering new content. Eclipse Marketing services help businesses understand and optimize these resource allocation decisions effectively.
How Search Engines Determine Crawl Budget for Each Website
Search engines base crawl budget decisions on two essential factors: crawl limit and crawl demand. These factors work together to create a balanced approach for website scanning priorities.
- Crawl limit or host load: This measures how much crawling your website can handle effectively. It also considers what preferences you have set as the website owner.
- Crawl demand or crawl scheduling: This determines which URLs deserve crawling the most frequently. Search engines evaluate this based on content popularity and how often updates occur.
Crawl budget represents a widely recognized term that SEO professionals use in their daily work. Some people also call crawl budget by other names like crawl space or crawl time interchangeably.
Does Crawl Budget Only Apply to Web Pages
Crawl budget actually covers more than just web pages, though we discuss pages for simplicity. In reality, crawl budget applies to any document that search engines need to examine. Other document examples include JavaScript files, CSS files, and mobile page versions specifically. Search engines also crawl hreflang variants and PDF files using your allocated crawl budget.
How Crawl Limit and Host Load Function in Real Website Situations
Crawl limit, which people also call host load, plays a crucial role in crawl budget allocation. Search engine crawlers actively work to prevent overwhelming web servers with too many requests simultaneously. They approach this process very carefully to maintain server stability and website performance consistently.
How do search engines actually determine your website’s crawl limit effectively?
Multiple factors influence crawl limit decisions that search engines make for each individual website.
- Signs of platform problems: Search engines monitor how frequently your requested URLs timeout completely. They also track how often your server returns error messages to their crawlers.
- The number of websites sharing your host: Your crawl limit becomes very restricted when multiple factors combine negatively. If your website operates on shared hosting with hundreds of other websites, problems increase significantly. When you also have a fairly large website, your crawl limit suffers even more. Crawl limits get determined at the host level, not the individual website level importantly. You must share your host’s total crawl limit with every other site running there. In this specific situation, you would benefit greatly from switching to dedicated server hosting. Dedicated hosting will also likely reduce loading times dramatically for all your website visitors.
Consider another important factor: having separate mobile and desktop sites on identical hosting platforms. These different versions share the same crawl limit between them, so plan accordingly.
How Crawl Demand and Crawl Scheduling Work in Real Website Management
Crawl demand, which people also call crawl scheduling, focuses on determining which URLs deserve re-crawling priority. Many different factors influence crawl demand decisions that search engines make for content evaluation.
- Popularity: Search engines measure how many internal links point to specific URLs on your website. They also count external links from other websites directing traffic to those pages. Additionally, they consider how many search queries each URL currently ranks for successfully.
- Freshness: Search engines track how frequently each URL receives updates and new content additions. Pages with regular updates receive higher crawl demand priority than static content consistently.
- Type of page: Different page types naturally change at varying frequencies throughout their lifecycle. Consider comparing a product category page with a terms and conditions page carefully. Which page do you think changes more often and deserves more frequent crawling attention? Understanding these patterns helps digital marketing agencies like those in Las Vegas develop targeted SEO strategies for different client industries.
Remember: Crawl Capacity Has System-Wide Limitations Too
Search engine crawling systems possess massive crawl capacity for handling billions of web pages. However, their total capacity still has definite limits that affect all website owners globally. Imagine a scenario where 80% of Google’s data centers go offline simultaneously without warning. Their overall crawl capacity would decrease dramatically in this situation, affecting every website’s crawl budget. All websites would experience reduced crawling frequency until full system capacity gets restored completely.

Why Crawl Budget Should Matter to Every Website Owner
You need search engines to discover and understand as many indexable pages as possible. You also want them to complete this process as quickly and efficiently as possible. When you publish new pages or update existing content, search engines should notice immediately. The faster they index your updated pages, the sooner you gain traffic benefits.
Wasting crawl budget prevents search engines from crawling your website effectively and thoroughly every time. They waste valuable time scanning unimportant parts of your site that provide no value. This inefficiency can leave crucial website sections completely undiscovered by search engine crawlers. When search engines don’t know specific pages exist, they cannot crawl or index them. You lose potential visitors who might find those pages through search engine results.
This situation creates a clear problem: wasting crawl budget directly damages your SEO performance significantly. Your website misses opportunities to attract organic traffic from search engines when important content remains hidden.
Remember that crawl budget concerns typically affect only large websites with substantial content volumes. Generally, you should worry about crawl budget optimization when your site exceeds 10,000 pages. For businesses in competitive markets like New Brunswick, even smaller sites benefit from understanding crawl budget principles to maximize their search engine visibility.
How to Find Your Website’s Crawl Budget Information
Google provides the most transparent crawl budget information compared to all other search engines available. They offer website owners clear insights into their crawling activity and frequency patterns.
Finding Crawl Budget in Google Search Console
You can access valuable crawl budget insights when your website gets verified in Google Search Console. This free tool provides detailed crawling statistics for your website’s Google performance.
Follow these simple steps to check your crawl budget:
- Sign into Google Search Console and select your specific website from the list.
- Navigate to Crawl then click on Crawl Stats to view your daily crawling data.
During summer 2016, one example website showed an average crawl budget of 27 pages daily. Using this average rate, the theoretical monthly crawl budget would equal 810 pages total. This calculation comes from multiplying 27 pages by 30 days in a month.
Two years later, that same website’s crawl budget increased dramatically to 253 pages daily. This represents a 10-times increase in crawl budget over just two years of operation.
Check Your Server Logs for Complete Crawling Data
Examining your server logs provides fascinating insights into Google crawler activity on your website. Server logs show exactly how frequently Google’s crawlers visit and scan your content. Always compare these server statistics with Google Search Console reports for accuracy verification. Using multiple data sources provides more reliable insights than relying on single sources. Search Engine Journal regularly publishes detailed guides on interpreting server log data for SEO optimization purposes.
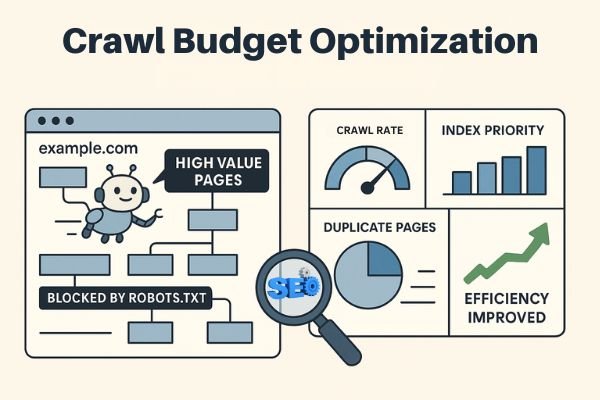
How to Optimize Your Crawl Budget Effectively
Crawl budget optimization focuses on eliminating all wasted crawl budget from your website completely. This means identifying and fixing every reason that causes crawl budget waste systematically. Professional SEO services monitor thousands of websites and reveal clear patterns in crawl budget problems that occur repeatedly. Most websites experience identical issues that damage their crawl budget efficiency significantly.
Here are the most common reasons for wasted crawl budget that website owners encounter:
- Accessible URLs containing parameters: Parameter URLs look like https://www.example.com/toys/cars?color=black in practice. These parameters often store visitor selections from product filters or search functions unnecessarily.
- Duplicate content problems: Pages that appear highly similar or exactly identical create duplicate content issues. Common examples include copied pages, internal search result pages, and tag pages specifically.
- Low-quality content pages: Pages containing very little meaningful content waste crawl budget significantly. Pages that provide no real value to visitors also fall into this category.
- Broken and redirecting links throughout your site: Broken links reference pages that no longer exist on your website. Redirected links point to URLs that automatically redirect visitors to different URLs instead.
- Including wrong URLs in XML sitemaps: Your XML sitemap should never include non-indexable pages or non-page content. This includes 3xx, 4xx, and 5xx status code URLs that waste crawler time.
- Pages with slow loading times or timeouts: Slow-loading pages negatively impact your crawl budget allocation from search engines. Pages that fail to load completely signal server problems to search engine crawlers. This causes search engines to reduce your crawl limit to protect your server.
- Too many non-indexable pages on your website: Websites containing excessive numbers of non-indexable pages waste valuable crawl budget resources unnecessarily.
- Poor internal link structure design: Incorrectly structured internal linking prevents search engines from properly prioritizing your important pages.
Managing URLs with Parameters to Save Crawl Budget
URLs containing parameters should remain inaccessible to search engines in most website situations completely. These parameter URLs can create virtually unlimited quantities of different URL combinations automatically. This problem gets discussed extensively in detailed articles about dangerous crawler traps online.
Product filters on eCommerce websites commonly use parameter URLs for customer browsing functionality. Using parameter URLs for filters works perfectly fine for user experience purposes. However, you must ensure search engines cannot access these parameter-based URLs at all.
How can you effectively block parameter URLs from search engine access completely?
- Use your robots.txt file to directly instruct search engines to avoid accessing parameter URLs. When robots.txt blocking isn’t possible for technical reasons, try alternative URL parameter settings. Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools offer URL parameter handling options specifically. These settings let you tell Google and Bing which specific pages to skip.
- Add the nofollow attribute value to all filter links throughout your website systematically. Remember that Google may choose to ignore nofollow directives since March 2020 policy changes. This makes completing step one even more critical for crawl budget protection.
Eliminating Duplicate Content to Protect Your Crawl Budget
Search engines shouldn’t waste time crawling duplicate content pages on your website ever. Preventing or minimizing duplicate content becomes essential for maintaining efficient crawl budget usage. Taking proactive steps protects your crawl budget from unnecessary waste and improves overall performance.
How can you effectively eliminate duplicate content from your website completely?
- Set up proper website redirects for all domain variants available to visitors. Configure redirects for HTTP, HTTPS, non-WWW, and WWW versions of your website consistently. This ensures search engines only crawl one canonical version of your content.
- Block internal search result pages from search engine access using robots.txt files. Internal search pages create unlimited duplicate content variations that waste crawl budget significantly. Your robots.txt file should prevent search engines from accessing these pages completely. Search Engine Land provides comprehensive tutorials on robots.txt implementation and best practices for blocking unwanted content.
- Disable dedicated image attachment pages that serve no real purpose for visitors. WordPress websites often create individual pages for every uploaded image by default. These image attachment pages rarely provide value and waste precious crawl budget resources.
- Use categories and tags carefully to avoid creating excessive duplicate content issues. Taxonomies like categories and tags can generate multiple pages with similar content automatically. Plan your taxonomy structure thoughtfully to minimize content duplication across different classification pages. Professional Google Ads management teams often encounter similar content optimization challenges when creating landing page variations for different campaigns.
Removing Low-Quality Content That Wastes Crawl Budget
Pages containing very little meaningful content fail to interest search engines at all. Keep these low-value pages to an absolute minimum or eliminate them completely when possible. Search engines prefer spending crawl budget on substantial, valuable content that serves real user needs.
One common example involves FAQ sections with poor structural design and implementation. Some websites create separate URLs for each individual question and answer combination unnecessarily. This approach generates multiple thin pages with minimal content that provides little value. Each question-answer pair gets its own dedicated URL, creating dozens of low-quality pages automatically. These thin content pages waste valuable crawl budget that could examine more important website sections. Instead, combine all FAQ content onto single, comprehensive pages that provide genuine value. Content Marketing Institute offers detailed strategies for creating substantial, valuable content that search engines prioritize during crawling.
Fixing Broken and Redirecting Links to Recover Crawl Budget
Broken links and lengthy redirect chains create dead ends that frustrate search engine crawlers completely. Google appears to follow a maximum of five chained redirects during single crawl sessions. They might resume crawling those redirect chains during later visits to your website. Other search engines handle subsequent redirects with varying levels of success and efficiency. However, avoiding chained redirects entirely and minimizing all redirect usage provides the safest approach.
Fixing broken links and redirecting links quickly recovers significant amounts of wasted crawl budget. Beyond crawl budget recovery, you also dramatically improve visitor user experience across your website. Redirects cause longer page loading times that directly hurt user experience and satisfaction. Chains of multiple redirects create even worse loading delays for your website visitors.
Finding broken and redirecting links becomes simple when you use proper website monitoring tools. Many SEO platforms provide dedicated sections for identifying these problematic links throughout your website. Look for link analysis features that highlight broken connections and redirect chains specifically.
Check your website’s link structure regularly to identify faulty links that waste crawl budget. Update each problematic link so it points directly to an indexable page instead. Remove links entirely when they no longer serve any useful purpose for visitors. This direct approach eliminates crawl budget waste while improving overall website performance and user experience.
Managing XML Sitemaps to Maximize Crawl Budget Efficiency
All URLs included in XML sitemaps must point to indexable pages that provide real value. Large websites especially depend on XML sitemaps to help search engines discover all important content. When XML sitemaps contain cluttered URLs that no longer exist or redirect elsewhere, precious crawl budget gets wasted. Regularly audit your XML sitemap for non-indexable URLs that don’t belong there at all. Also check for the opposite problem: important pages incorrectly excluded from your XML sitemap. XML sitemaps offer excellent opportunities to guide search engines toward wise crawl budget spending.
XML Sitemap Issues in Google Search Console
Follow these steps to locate XML sitemap problems in Google Search Console effectively:
- Sign into Google Search Console and select your website from the dashboard.
- Navigate to Indexing then click on Sitemaps to view your submitted sitemaps.
- Click on your specific XML sitemap to examine its performance and status.
- Click on SEE PAGE INDEXING to review detailed indexing reports for sitemap URLs.
Locating XML Sitemap Issues in Bing Webmaster Tools
Use these steps to find XML sitemap problems in Bing Webmaster Tools:
- Log into your Bing Webmaster Tools account and select your verified website.
- Click the Configure My Site tab from the main navigation menu options.
- Click the Sitemaps tab to access all sitemap-related reports and analysis tools.
Using ContentKing for XML Sitemap Analysis
ContentKing provides comprehensive XML sitemap monitoring through these simple steps:
- Access your ContentKing account dashboard and select your monitored website project.
- Click the Issues button to view all detected website problems and recommendations.
- Click the XML Sitemap button to focus specifically on sitemap-related crawl budget issues.
- When pages have sitemap problems, you’ll receive this clear message: Page is incorrectly included in XML sitemap.
Best Practice: Split Large XML Sitemaps into Smaller Section-Based Files
Dividing XML sitemaps into smaller, section-specific files improves crawl budget optimization significantly. Create separate XML sitemaps for each major website section to enable better monitoring. This approach helps you quickly identify problematic sections that waste crawl budget unnecessarily.
Consider this example: Section A’s XML sitemap contains 500 links with 480 successfully indexed. This represents excellent performance with minimal crawl budget waste occurring there. However, Section B’s XML sitemap contains 500 links but only 120 get indexed successfully. This dramatic difference signals serious problems worth investigating immediately in Section B. You likely included many non-indexable URLs in Section B’s XML sitemap wastefully.
Fixing Slow Loading Pages That Damage Your Crawl Budget
Pages with slow loading times and timeouts seriously damage the entire crawling process. When pages load slowly or fail to load completely, search engines visit fewer pages. This reduces the effective use of your allocated crawl budget significantly every day. Beyond crawl budget problems, slow page speeds dramatically hurt visitor user experience completely. Poor loading times directly result in lower conversion rates and lost revenue opportunities.
Page loading times above two seconds create serious problems that require immediate attention. Ideally, every page should load in under one second for optimal performance results. Regularly monitor your page loading speeds using reliable tools like Pingdom, WebPagetest, or GTmetrix. These tools provide detailed insights into what slows down your website performance.
Google provides page loading time reports in two different locations for comprehensive monitoring. Google Analytics shows this data under Behavior then Site Speed for visitor experience insights. Google Search Console displays crawler-specific loading data under Crawl then Crawl Stats sections.
Both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools report page timeout issues clearly. Google Search Console shows timeout data under Settings then Crawl Stats for detailed analysis. Bing Webmaster Tools displays this information under Reports & Data then Crawl Information respectively.
Check your page loading speeds regularly to ensure optimal performance across your entire website. Take immediate corrective action when pages fail to meet acceptable speed standards consistently. Fast-loading pages remain absolutely vital to your online success and crawl budget efficiency. Professional web design services can help optimize your site’s loading speeds and overall performance.
Reducing Non-Indexable Pages That Waste Crawl Budget Resources
Websites containing excessive numbers of non-indexable pages force search engines to waste time. Search engines spend valuable crawl budget examining irrelevant pages that provide no indexing value. This inefficient process reduces the time available for crawling your important, indexable content.
The following page types count as non-indexable pages that waste crawl budget unnecessarily:
- Redirect pages returning 3xx status codes that send visitors elsewhere automatically
- Missing pages returning 4xx errors when requested content cannot be found
- Server error pages returning 5xx codes due to technical problems or outages
- Pages containing robots noindex directives or canonical URLs pointing to different locations
Finding your website’s ratio of non-indexable pages requires analyzing total discovered URLs carefully. Website monitoring tools can break down these numbers to show indexable versus non-indexable ratios. For example, one website analysis revealed 63,137 total URLs discovered by crawlers. However, only 20,528 of those URLs represented actual pages worth examining further.
From those pages, only 4,663 qualified as indexable content for search engines. This means only 7.4% of all discovered URLs could actually get indexed successfully. Such poor ratios indicate serious crawl budget waste that requires immediate cleanup action.
Fix this problem by removing unnecessary references to non-indexable pages throughout your website:
- Clean up your XML sitemap by removing non-indexable URLs completely
- Remove internal links pointing to non-indexable pages that waste crawler time
- Fix canonical URLs that reference non-indexable destinations incorrectly
- Remove hreflang references pointing to non-indexable language variations or regions
- Clean up pagination references using link rel prev/next that point to non-indexable pages
Improving Internal Link Structure for Better Crawl Budget Distribution
How pages connect to each other within your website significantly impacts crawl budget optimization. This connection system gets called the internal link structure of your website. Beyond external backlinks, pages with fewer internal links receive much less search engine attention. Pages linked by many other pages get prioritized during crawling sessions consistently.
Avoid creating overly hierarchical link structures where middle-tier pages receive few internal links. These poorly connected pages often get crawled infrequently by search engine bots. Pages at the bottom of deep hierarchies face even worse problems completely. Their limited internal links cause search engines to neglect them during regular crawling.
Ensure your most important pages receive plenty of internal links from throughout your website. Recently crawled pages typically achieve better search engine rankings than neglected content. Keep this principle in mind when designing your internal link structure strategically.
Consider this example: you have a blog article from 2011 that still drives significant organic traffic. Keep linking to this valuable content from newer articles and relevant pages regularly. Publishing many new blog articles over the years automatically pushes older content down. This happens because newer content naturally receives more internal links from recent publications. Your 2011 article loses internal link equity and crawl priority without deliberate linking efforts. Actively maintain links to high-performing older content to preserve its crawl budget allocation.
How to Increase Your Website’s Crawl Budget Allocation
Google’s former head of webspam team Matt Cutts discussed the relationship between authority and crawl budget. During an interview with Eric Enge, this important connection got explained clearly. Google stopped updating PageRank values publicly, but similar authority calculations likely remain in their algorithms. Since PageRank confuses many people, we can call this concept page authority instead. Matt Cutts essentially confirmed that page authority and crawl budget have a strong relationship.
Therefore, increasing your website’s crawl budget requires building your website’s overall authority systematically. Earning more links from external websites represents a major part of this authority building. High-quality backlinks from reputable websites signal to search engines that your content deserves attention. Search engines reward authoritative websites with larger crawl budgets to examine their content thoroughly.
Focus on creating valuable content that naturally attracts links from other websites in your industry. Build relationships with other website owners who might reference your content appropriately. Guest posting on relevant websites can also help establish your authority and earn backlinks. Remember that quality matters more than quantity when building external links for authority.
More comprehensive information about effective link building strategies can help you develop systematic approaches. These strategies focus on earning legitimate links that genuinely increase your website’s authority over time. Working with experienced Google consulting services can accelerate your authority building efforts and crawl budget optimization results.
Conclusion
Optimizing your crawl budget directly impacts your website’s SEO performance and search engine visibility significantly. Search engines allocate limited resources across millions of websites, making efficient crawl budget usage essential for success. Focus on eliminating common crawl budget waste through parameter URL management, duplicate content removal, and broken link fixes. Improve your internal link structure to guide crawlers toward your most valuable pages strategically. Monitor page loading speeds regularly and maintain clean XML sitemaps for optimal crawler guidance. Remember that crawl budget optimization primarily benefits large websites exceeding 10,000 pages effectively. Building website authority through quality backlinks increases your crawl budget allocation over time naturally. Take immediate action to audit your website for these common issues today. Implementing these proven strategies ensures search engines discover and index your important content efficiently. Your improved crawl budget optimization will drive better SEO performance and increased organic traffic consistently. For professional assistance with crawl budget optimization and comprehensive SEO strategies, contact our team to maximize your website’s search engine potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is crawl budget and why does it matter for SEO?
Crawl budget represents the number of pages search engines examine on your website daily. When you waste crawl budget, search engines cannot discover your important content effectively. This directly damages your SEO performance and reduces search engine visibility significantly.
How can I check my website’s current crawl budget allocation?
Google Search Console provides the most transparent crawl budget information for website owners. Sign into your verified account and navigate to Crawl then Crawl Stats sections. Additionally, examine your server logs to compare with Google Search Console data.
What are the most common reasons websites waste their crawl budget?
Parameter URLs create virtually unlimited URL combinations that waste crawler time significantly. Duplicate content forces search engines to examine similar pages repeatedly without adding value. Broken links and redirect chains create dead ends that frustrate crawler efficiency.
Should small websites worry about crawl budget optimization at all?
Crawl budget concerns primarily affect large websites with substantial content volumes typically. Generally, worry about crawl budget when your website exceeds 10,000 pages total. However, following basic optimization practices still benefits websites of all sizes.
How can I increase my website’s crawl budget over time?
Building website authority through quality backlinks increases your crawl budget allocation significantly. Create valuable content that naturally attracts links from reputable websites consistently. Focus on earning legitimate links rather than using manipulative tactics.

Mike has over 5 years of experience helping clients improve their business visibility on Google. He combines his love for teaching with his entrepreneurial spirit to develop innovative marketing strategies. Inspired by the big AI wave of 2023, Mike now focuses on staying updated with the latest AI tools and techniques. He is committed to using these advancements to deliver great results for his clients, keeping them ahead in the competitive online market.