What Makes AI SEO Different From Traditional SEO Tactics?
AI SEO differs from traditional SEO in five fundamental ways: query length, search behavior, content evaluation, optimization focus, and data processing methods. Traditional SEO targets 4-5 word keyword phrases through page-level optimization, while AI SEO handles 23-word conversational prompts using passage-level analysis.
The key differences include user behavior patterns, where traditional search involves single isolated queries compared to AI’s multi-turn conversations that retain context. Content optimization has shifted from keyword matching to topic coverage and semantic relevance. AI systems now evaluate individual passages rather than entire pages, requiring structured sections with clear H2s and H3s.
Statistical evidence shows AI SEO’s superior performance: 44.1% of core SEO tasks are now automated, 75.4% of professionals report improved operational scaling, and 49.2% achieved better rankings after Google algorithm updates. Only 30% of AI search queries fit traditional intent categories, with 70% representing mixed or entirely new search purposes.
Traditional search engines provide ranked lists of multiple pages, while AI search generates single synthesized answers that reference and link to sources. This fundamental shift requires SEO strategies focused on conversational variations, topic clusters, and content formatted for AI synthesis rather than featured snippets.
Modern SEO success depends on understanding both systems: traditional foundations for keyword relevance and AI capabilities for natural language processing, topic authority, and passage-level optimization that serves both human users and AI systems effectively.
How People Search: Traditional Methods vs AI
AI has completely transformed how people use search engines. These changes appear in query phrasing and expected results. Let’s examine the differences and how they impact search engine optimization strategies.
Search Style: Brief Keywords vs Natural Conversations
Traditional search engines trained users to think in keywords. We learned to type short phrases like “best pizza NYC” or “fix leaking faucet.” The average traditional search query uses just 4-5 words. Users simplified their language because search engines could only understand basic terms.
AI search has flipped this pattern completely. People now write searches as if they’re talking to another person. ChatGPT prompts average 23 words – almost five times longer than old-style searches. This shows how AI lets people communicate naturally.
“I need a 10K training plan, I’ve got two weeks, I already play football, I want to keep doing that. What should I do?” This sounds like real conversation, not the robotic way we used to search.
The data supports this shift. Searches with 8+ words have grown seven times larger. Technical phrasing has increased 48%. Instead of typing “best AI SEO tool,” people ask questions like: “What’s the best AI SEO tool under USD 30.00/month for researching the questions people have about a brand?”
Search Goals: Finding Pages vs Completing Tasks
Traditional search engines organize user intent into four main groups:
- Navigational: Finding specific websites (“Facebook login”)
- Informational: Learning about topics (“how to change a flat tire”)
- Commercial: Researching products (“best laptop for gaming”)
- Transactional: Making purchases (“buy iPhone 16 Pro”)
These categories worked well for years. AI search shows they don’t tell the complete story. Studies reveal only 30% of ChatGPT queries fit these standard groups. The other 70% represent mixed or completely new types of intent.
Traditional search engines often miss the target on user intent. They mostly match keywords instead of understanding context. AI search engines use natural language processing to grasp both context and intent, which leads to better results.
Product research shows this difference clearly. Traditional search needs several separate queries – “best smartphones 2025,” “smartphone camera comparison,” “top phones under USD 1000.00”. AI search handles one specific question: “What are the top 3 smartphones for photography under USD 1000.00?”
AI search optimization focuses on completing tasks rather than just finding information. Users want to solve problems and reach goals, not just collect facts.
Search Interaction: Single Searches vs Ongoing Conversations
The biggest change appears in how interactions develop over time. Traditional search follows a simple pattern: type query, look at results, click link, maybe try a new search. Each search stands alone, forgetting what came before.
“Traditional search engines don’t dynamically evolve based on user interactions. Once you click on a link, the search engine doesn’t adjust its results in real-time”. Users must start fresh with every new search.
AI search creates an ongoing conversation. People ask questions and follow up naturally, referring to earlier exchanges. The AI remembers everything from the session, so users don’t repeat themselves.
A laptop search shows this well. After the first question, typing “not mac” makes sense because the AI remembers you’re looking at laptops. Later, “and a backpack for it” automatically means a laptop bag that fits your choice.
This context awareness turns isolated searches into real conversations. Users don’t need to visit multiple sites and piece information together. They can let the AI do this work through continued dialog.
Search optimization must adapt to these changes. Content should answer follow-up questions and connect related topics smoothly. SEO strategies must consider how information fits into longer conversations.
AI systems can handle complex questions automatically. Google’s answer method “can break down compound queries, such as ‘What is Google Cloud and Google Ads respective revenue in 2024?’ into multiple, smaller queries to return better results”. Users don’t need to simplify their questions anymore.
Businesses must change their optimization approach. Content needs to cover conversational variations, multiple purposes, and connected topics. AI search optimization requires understanding extended dialogs instead of single searches.
Multi-turn sessions might mark the biggest shift in search behavior since keyword engines began. One expert notes, “As the result content changes underneath me, so too does my expectation of what I will get”. These new expectations create fresh challenges and opportunities for search strategy experts.

Content Optimization Methods
Search success still depends on content optimization, though traditional and AI-driven search take completely different approaches. The basic techniques have evolved beyond simple keyword matching into advanced topic modeling. Let’s explore these key differences.
Keyword Focus vs Complete Topic Coverage
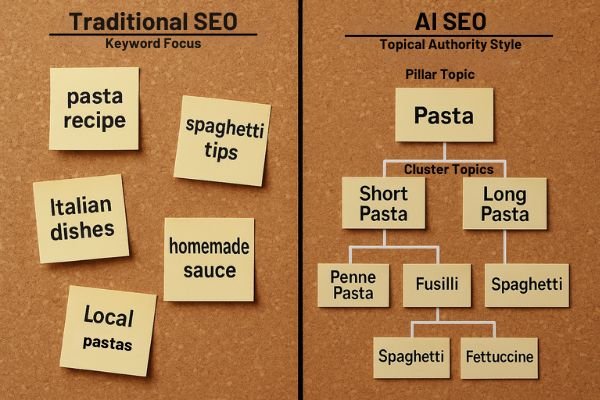
Traditional search engine optimization heavily relied on keyword optimization – finding exact phrases users type into search boxes. SEO specialists did manual research to find terms that matched user needs, from informational to transactional queries. This keyword-first approach created separate pages for each keyword variation, which often produced thin content serving algorithms better than readers. “Stop thinking of keyword phrases and reorient your strategy around topics and themes,” advises one expert.
This shift shows how AI search has changed content prioritization. Traditional SEO mainly focused on: Finding and targeting specific keywords Strategic keyword placement Metadata optimization Alt tags and link structures
AI search values semantic relevance and topical authority more. Research shows that “AI systems assess content based on meaning, not just keyword matching”. Pages with loose connections to queries don’t make the cut, whatever their keyword density.
The difference becomes clearer in how each approach handles content:
Keyword-First Strategy:
- Targets individual terms alone
- Creates standalone pages for each keyword variation
- Results in disconnected content pieces
- Looks like “whack-a-mole” optimization
Topic-First Strategy:
- Organizes content around central themes
- Creates complete topic clusters
- Answers related questions
- Shows depth and expertise
Data reveals websites with complete topic coverage usually rank for 2-3 times more keywords than those targeting isolated terms. Additionally, pages that thoroughly cover topics often rank for keywords not even in the content – showing how AI understands context beyond exact matches.
Here’s one practical difference: Rather than making separate pages for “homemade penne pasta recipe” and “how to make spaghetti,” a topic-first approach would put both under broader categories like “Pasta Shapes → Short Pasta” and “Pasta Shapes → Long Pasta”. This structure signals authority to AI systems.
Page Focus vs Section-Level Relevance
The most important change in optimization techniques involves how content gets evaluated. Traditional search looked at entire pages as single units. Pages had to show relevance as a whole to rank well.
AI search, with developments like passage indexing, looks at content in much smaller pieces. “LLMs blend relevant passages across the web instead of retrieving full web pages from an index”. Each content section should now answer a specific user question or intent.
Section-level optimization means:
- Individual sections must stand alone
- Each paragraph should provide clear, targeted information
- Weak sections get ignored, even on well-ranked pages
One source explains, “With the introduction of Passage Indexing, Google’s algorithm now understands the context and relevance of specific passages within a page, regardless of the rest of the content”. Pages covering multiple topics can rank for queries about individual sections.
Content creation has changed significantly. Good AI search SEO needs well-organized sections that each tackle distinct subtopics or questions, rather than optimizing whole pages around single topics. “Break content into digestible, intent-focused sections,” says one expert. “Structure your articles with clear headings describing the covered content”.
A long-form article about smartphone photography might have targeted just “smartphone photography tips” before. Now, each passage should answer specific questions: “How to take low-light photos with smartphones,” “Best smartphone camera settings for portraits,” etc. AI can then find exactly what matches each user query.
Formatting for Snippets vs Formatting for AI Understanding
Formatting matters in both traditional and AI search optimization, but with different goals. Traditional SEO formats content to win featured snippets – those answer boxes at the top of search results.
This usually means:
- Writing direct answers to common questions
- Using structured data and FAQ schema
- Making bullet points or numbered lists
- Putting clear definitions first
Featured snippets show information exactly as written on your page. Optimization meant presenting information in the exact format for Google to display.
AI search transforms content instead of just showing it. AI Overviews generate a synthesized response by pulling insights from multiple sources… The information changes through AI rather than appearing as-is”. This fundamental difference needs new formatting approaches.
AI synthesis optimization works better with:
- Content in structured sections with clear H2s and H3s
- Quick answers in each passage
- Bullet points, tables, or clear formatting that helps LLM parsing
- Relevant schema markup for context
AI systems like content that’s “structured and easy to scan”. Elements like bullet points, numbered lists, and tables make content clearer and easier for AI to extract key points.
The difference shows in how they extract information. Traditional snippets copy exact content pieces. AI synthesis learns meaning from multiple sources before creating new text with the main ideas. Your formatting should help this understanding instead of providing ready-made snippets.
AI search also values content with multimedia elements. AI can learn from images, tables, and videos, making inclusion more likely”. This opens new ways to optimize visual content alongside text.
Passage-level optimization means formatting smaller content units too. Focus on making each section complete and clearly structured instead of optimizing entire pages. “To optimize for Passage Indexing, identify key passages that directly address specific topics or questions”.
The move from traditional to AI search optimization represents a fundamental shift in approach. One expert puts it this way: “AI SEO uses machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and analytical algorithms to optimize content, analyze trends, and improve rankings”. These capabilities need content that’s organized, complete, and rich in meaning rather than just keyword-optimized.
The future of search engine optimization belongs to content serving both humans and AI through thoughtful structure, meaningful topics, and clear formatting that helps understanding at both page and passage levels.

How AI Is Revolutionizing Data Handling and SEO Analysis
From Manual Spreadsheets to Automated Intelligence
Modern SEO strategies rely on powerful data analysis. Today, many marketers and SEO teams choose AI over manual tools. The reason is simple – AI spots trends and anomalies in massive datasets that humans might miss. Around 44.1% of SEO tasks like content creation and keyword research are now automated.
The old process of copying and pasting into spreadsheets is not only time-consuming – it’s inefficient. One expert explained it clearly: “Copying and pasting into spreadsheets is not the best use of time.” Manual analysis may never be as detailed without taking significant effort.
AI tools analyze vast amounts of SEO data instantly. They flag issues in real time, allowing your team to focus on strategy, not data crunching. Instead of hours spent building reports, AI delivers answers within seconds.
AI Outperforms Traditional SEO Methods
The shift to automation offers more than just convenience – it gives marketers a competitive edge. AI excels at:
- Live performance monitoring: It tracks hundreds of metrics and highlights anomalies before they affect rankings.
- Pattern recognition: It finds insights across campaigns that humans may overlook.
- Predictive analysis: AI forecasts future trends and user behavior for smarter planning.
Adaptability: It reacts faster to search algorithm updates.
Compared to traditional SEO analysis, manual methods require more time, people, and effort. They’re slower, less accurate, and difficult to scale. AI changes that. According to industry surveys, 75.4% of professionals say AI has improved their SEO results. Nearly 49.2% of them noticed ranking improvements after recent Google updates – thanks to AI’s rapid adaptation.
AI also connects the dots between different SEO activities. It reveals how one tweak affects hundreds of variables, offering clear insights into what’s actually driving growth.
Better Reporting, Smarter Local Targeting, and Cost Efficiency
Reporting has come a long way. While spreadsheets like Excel are still used for flexibility, they’re not built for deep analysis. Creating meaningful visuals takes time – and often lacks visual impact.
AI reporting tools do more. They pull data directly from sources like Google Analytics, social media, and ad platforms. Dashboards offer rich visuals – charts, tables, and KPIs – making year-to-year comparisons easier. Plus, they’re responsive across all devices.
AI also enhances local SEO. It uses geolocation data to fine-tune Google Business Profiles, improving visibility in local searches. Targeting specific regions becomes easier and more accurate.
Cost is another factor. While AI platforms may seem expensive at first, they pay off long term. Manual work costs more over time due to the hours required. AI reduces that need and offers plain-language reports, making technical data accessible to non-experts on your team.
Lastly, AI is a valuable ally for competitor research. It uncovers hidden opportunities in their keyword strategy, content gaps, and backlink profiles. Manual analysis can’t keep up with AI’s speed, depth, and responsiveness.
Comparison Chart
| Area | Traditional SEO | AI SEO |
| Query Length | 4-5 words | 23 words on average |
| Search Style | Keyword-based fragments | Natural conversation prompts |
| User Intent Categories | 4 fixed categories (Navigational, Informational, Commercial, Transactional) | 70% of queries fall outside traditional categories |
| Search Session Type | Single, isolated queries | Multi-turn conversations that retain context |
| Content Focus | Keyword matching and placement | Topic coverage and meaning relevance |
| Content Evaluation | Page-level assessment | Passage-level analysis |
| Content Structure | Optimized for featured snippets | Formatted for AI synthesis |
| Data Processing | Manual analysis with spreadsheets | Immediate automated processing |
| Analysis Speed | Hours for simple analysis | Instant results |
| Pattern Recognition | Limited to human observation | Automated trend detection |
| Adaptation to Updates | Slow manual adjustments | Immediate strategy changes |
| Task Automation | Minimal automation | 44.1% of core SEO tasks automated |
| Performance Impact | Not mentioned | 75.4% report improved operational scaling |
| Ranking Improvements | Not mentioned | 49.2% better rankings after algorithm updates |
Conclusion
The transition from traditional to AI-powered SEO represents more than a technical upgrade – it’s a complete reimagining of search optimization. Traditional methods focusing on keyword matching and page-level optimization are giving way to conversational queries and passage-level relevance. AI search has fundamentally changed user behavior, with queries becoming 23 words on average compared to traditional 4-5 word searches. The data speaks volumes: 44.1% of SEO tasks are now automated, 75.4% of professionals report improved scaling, and 49.2% see better rankings after algorithm updates. Success in this new landscape requires understanding topic clusters over isolated keywords, optimizing for conversations rather than single queries, and formatting content for AI synthesis instead of featured snippets. The future belongs to SEO professionals who master both traditional foundations and AI capabilities to create comprehensive, user-focused strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main difference between traditional SEO and AI SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on keyword matching and page-level optimization. AI SEO emphasizes conversational prompts and passage-level relevance. AI systems analyze content meaning rather than just keyword density.
2. How has user search behavior changed with AI search engines?
Users now write conversational queries averaging 23 words instead of 4-5 word phrases. They engage in multi-turn conversations that retain context. People ask complete questions like talking to another person.
3. Should I stop using keywords entirely for AI SEO?
No, keywords remain important but the approach has evolved significantly. Focus on topic clusters and semantic relevance rather than exact matching. Create comprehensive content covering related themes instead of separate pages.
4. How does AI evaluate content differently than traditional search engines?
AI evaluates content at the passage level rather than entire pages. Each section must stand alone and answer specific questions. Traditional search looks at overall page relevance while AI extracts meaningful passages.
5. What formatting changes should I make for AI search optimization?
Structure content with clear H2s and H3s for better AI understanding. Use bullet points, tables, and organized formatting that helps information extraction. Include multimedia elements since AI can learn from them.

Mike has over 5 years of experience helping clients improve their business visibility on Google. He combines his love for teaching with his entrepreneurial spirit to develop innovative marketing strategies. Inspired by the big AI wave of 2023, Mike now focuses on staying updated with the latest AI tools and techniques. He is committed to using these advancements to deliver great results for his clients, keeping them ahead in the competitive online market.