SEO That Brings In Sales
No fancy reports that mean nothing
No vanity numbers that don’t lead to revenue
- No marketing fluff
Most agencies hand you pretty dashboards and big promises but zero real customers.
We build your online presence so Google and ChatGPT trust you enough to send you traffic that turns into actual sales.
Here’s what we cover in the video:
- Why some agencies promise you easy keywords like “Asian Home Remodeler in Montgomery Alabama” — keywords nobody actually searches for, so they’re easy to rank.
- How we guarantee Top 3 rankings for competitive keywords like “Home Remodelers in Dallas” — or you don’t pay. (More on the guarantee below.)
- How we repeat this across tough niches like home remodeling, roofing, and product businesses.
$20M+
Revenue Generated for Clients
100+
Documented Case Studies
2.6 Yrs
Avg. Client Retention
Top 3
Rankings or You Don’t Pay



Our Top 3 Guarantee
We don’t rank you for keywords your customers will never search.
We target the exact terms people type in when they’re ready to hire — keywords like “Home Remodelers in Dallas” or “Kitchen Renovation Near Me.”
The guarantee is simple: we get you into the Top 3 on Google for your target keywords, or you don’t pay for SEO that month.
How we pull it off:
- Keyword selection that matches buyer intent — we pick terms people search when they’re ready to spend, not just browse.
- Review generation at scale — Google’s local algorithm heavily weights reviews. We help you build a steady stream of real 5-star reviews that push you above competitors.
- Technical SEO + content that converts — fast site, clean structure, and pages built to turn visitors into booked calls.
- AI-powered execution — we move 3x faster than traditional agencies because we use AI at every stage of the process.
This isn’t a gimmick. We’ve done it across 100+ campaigns. If we can’t do it for you, we’ll tell you upfront on the strategy call.
We're A Founder Led Agency
Here’s the good and the bad of working with us:
The Good
The Bad
Ready to See What SEO Can Do for Your Business?
We’ll audit your current rankings, show you where you’re leaving money on the table, and map out a plan to fix it. No pressure, no pitch deck.





Why SEO Matters
SEO is a real asset that lives on the internet.
Picture the #1 ranked “Home Remodeling Company in Dallas, Texas.”
That company gets leads while the owner sleeps.
It’s an asset worth 3–5x in valuation if you ever sell.
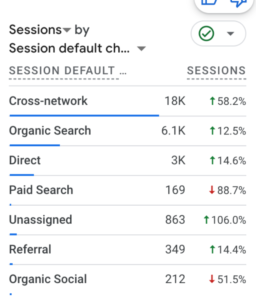
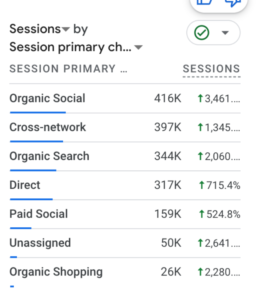
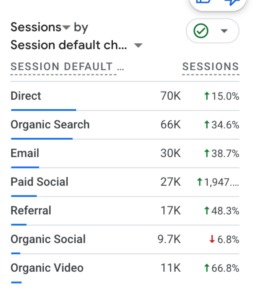
Our 3-Step Process
We Find Keywords That Drives Sales
There’s a difference between keywords that look good on paper and keywords that bring in paying customers. We only target the ones that make you money.
We Study Your Top Competitors
No need to start from scratch. We look at what’s already working for the top players in your space, take the best parts, and put them to work for you.
We Use AI to Move Faster
What used to take months now gets done in days. We use the latest AI tools to speed up every step without cutting corners.
SEO for Google and AI Search
Search has changed. Older folks say “Google it.” Younger folks say “Search it” — and they’re using ChatGPT, not Google.
Modern SEO needs to work across:
- Google Search
- ChatGPT
- AEO and GEO (AI and generative engine optimization)
If those terms are new to you, that’s fine. Think of it like the SEO gold rush of 2005. Most people haven’t caught up yet, and the ones who move first win the most.



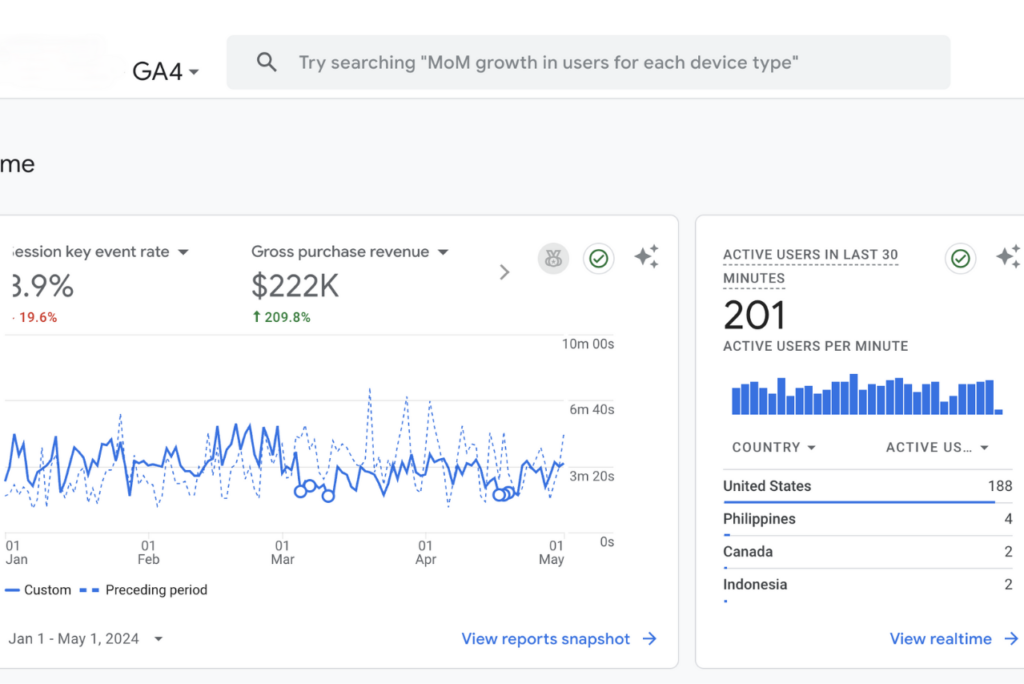
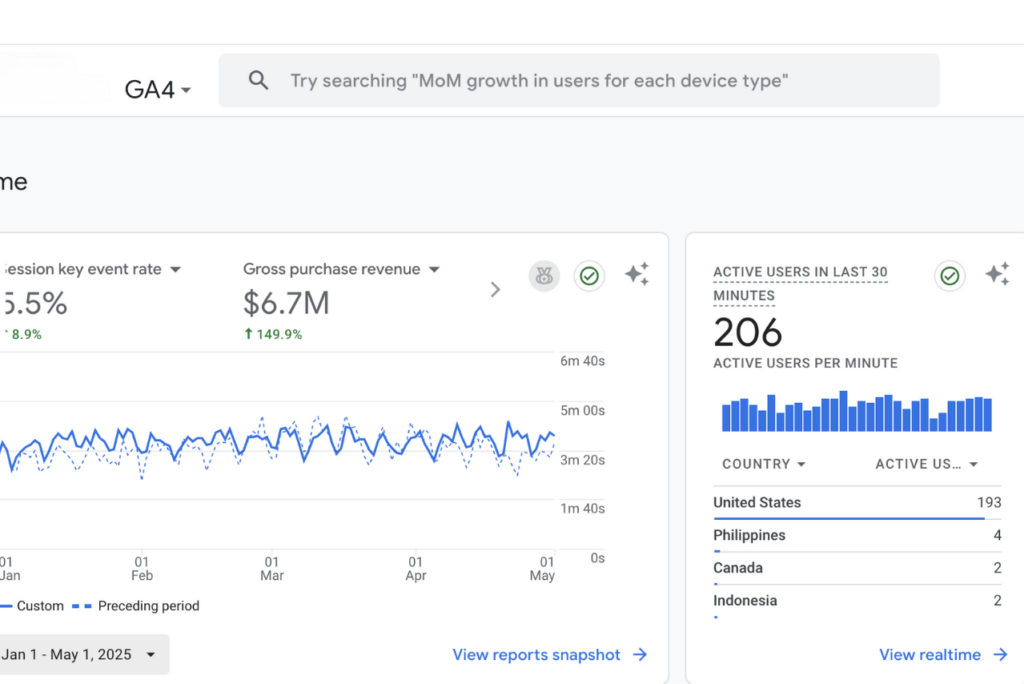
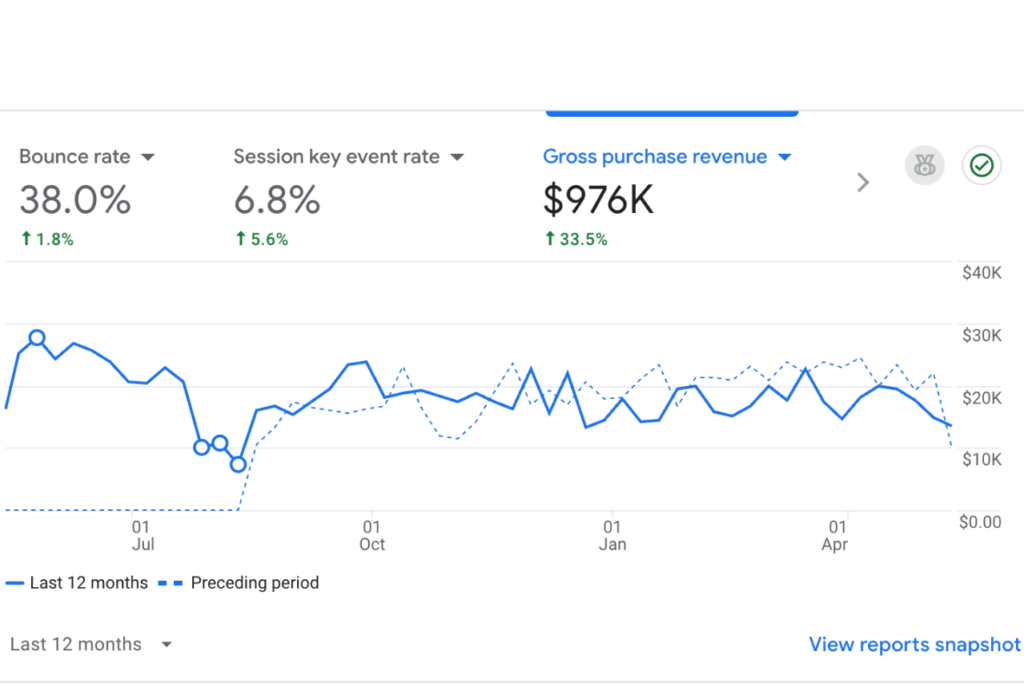
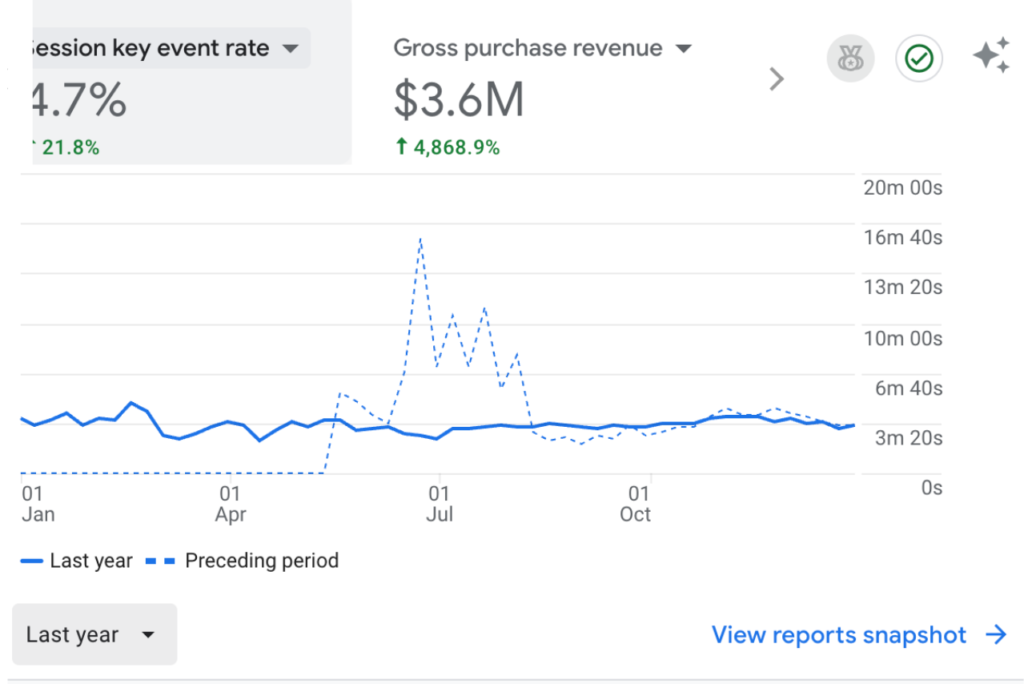
Results That Matter
Over the last 6+ years:
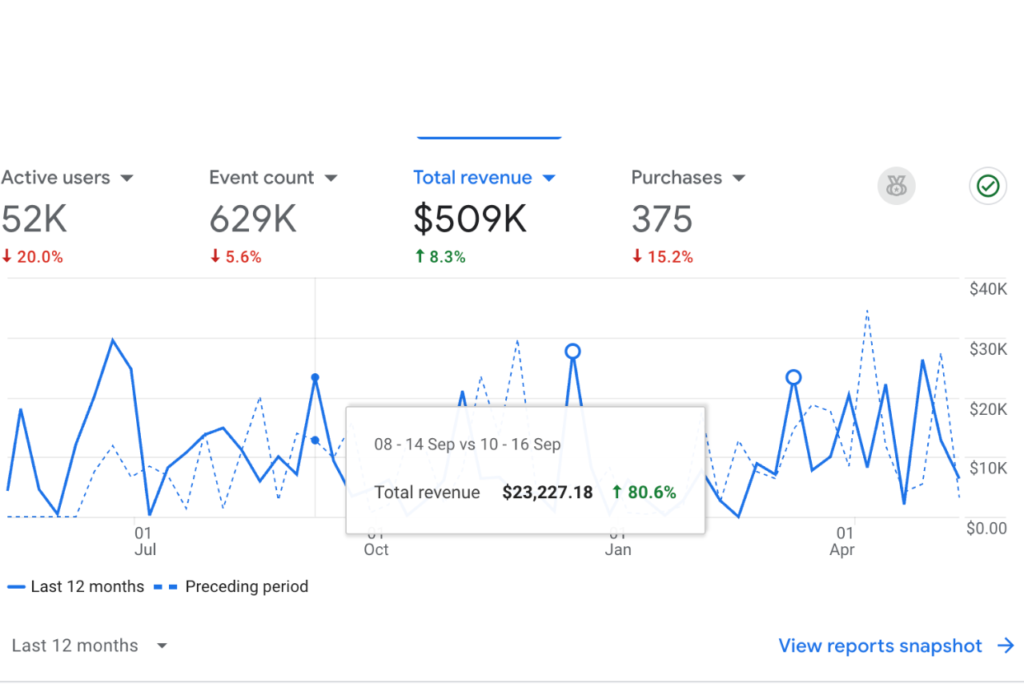
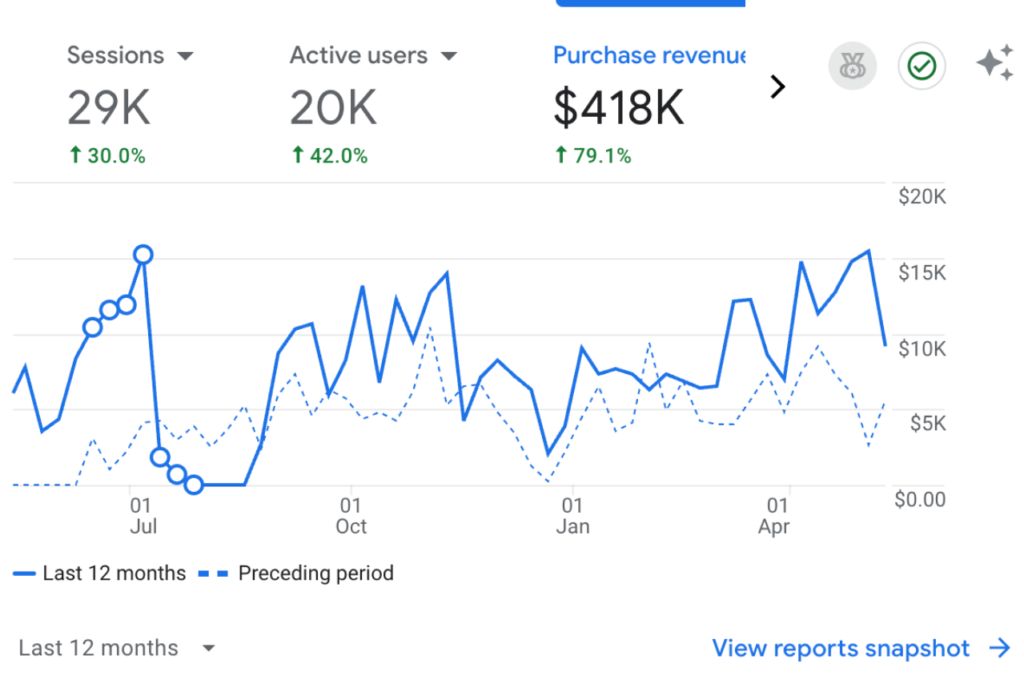
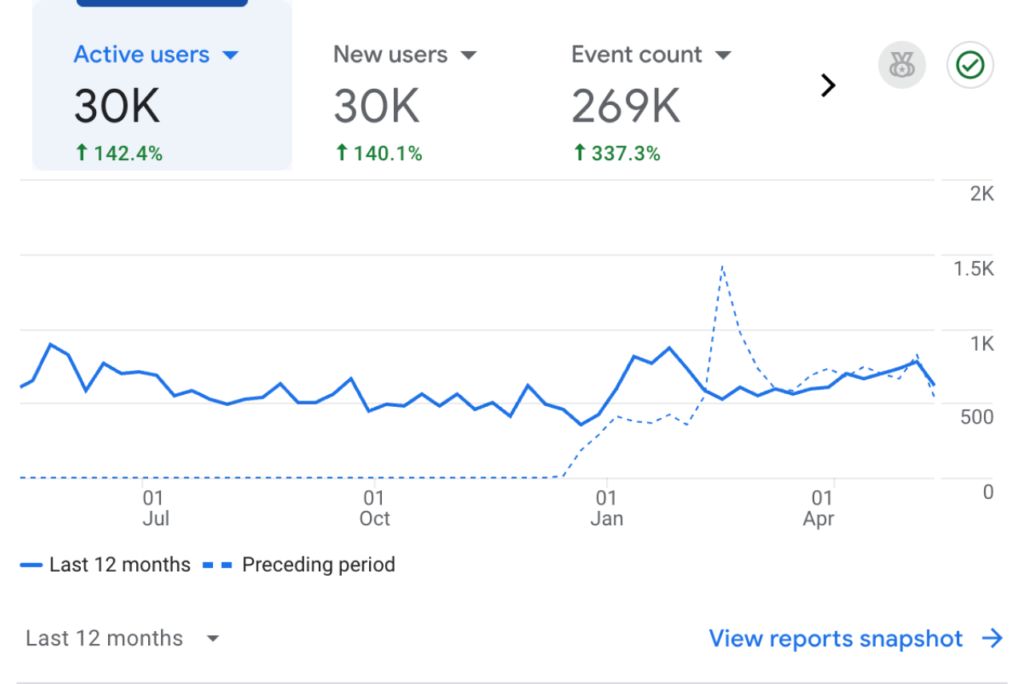
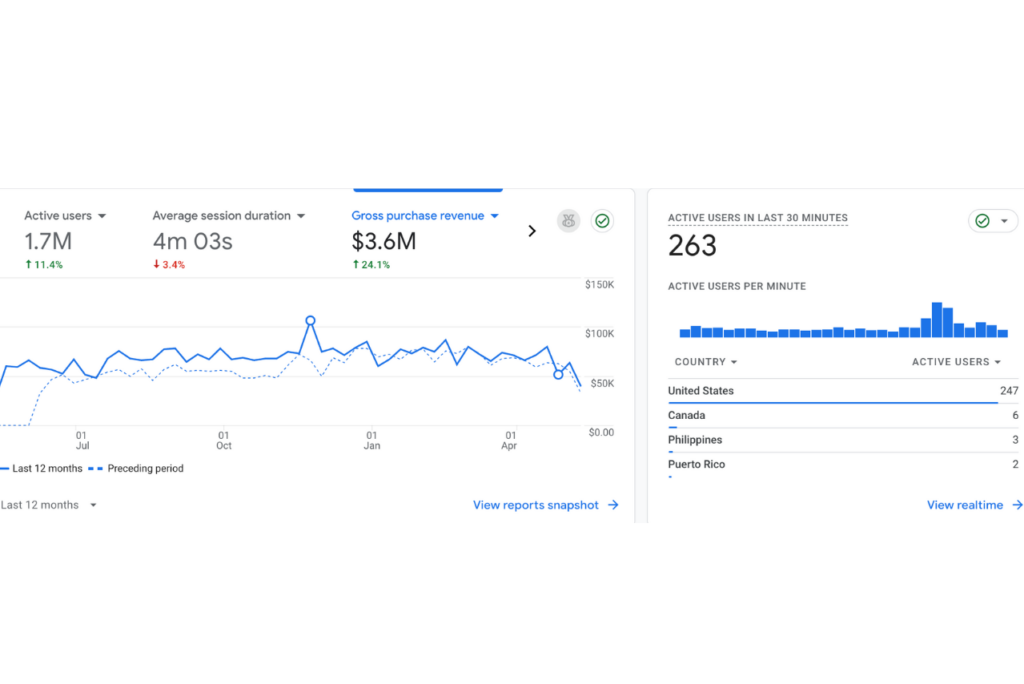
What This Looks Like for Home Remodelers:
Case Study: Dallas Kitchen & Bath Remodeler
Before
12 leads/month
After (8 Months)
67 leads/month
Revenue Impact
+$840K/year
Ranked #1 for “kitchen remodeling Dallas” and #2 for “bathroom renovation Dallas.”
Went from 45 Google reviews to 210+ in 8 months.
Average job value: $38K. SEO now drives 40% of new business.
Case Study: Houston Full-Service Remodeler
Before
800 visits/month
After (8 Months)
4,200 visits/month
Revenue Impact
+$1.2M/year
Ranked Top 3 for 14 high-intent keywords across Houston metro.
Cost per lead dropped from $186 to $42 after replacing paid ads with organic.
Now expanding to 3 new service areas using the same playbook.
Case Study: Phoenix Roofing & Exterior Remodel
Before
22 Google reviews
After (8 Months)
185 Google reviews
Revenue Impact
+$520K/year
Moved from page 3 to Map Pack for “roofing company Phoenix.”
Organic leads now outperform Angi and HomeAdvisor leads by 3x on close rate.
Owner cut ad spend by $4K/month while growing revenue.
Who Is This For?
SEO works best for businesses doing at least $1M+ per year in revenue.
Most agencies will sell anyone a cheap retainer. They just want your money. We’re different.
Good Fit:
- Your business already makes money.
- You have a working customer channel and want to add another one. (SEO should not be your first channel.)
- You’re a local business looking to grow into more locations.
Not a Fit:
- You want a quick fix and aren’t ready to build a long-term asset.
- You don’t have a working sales channel and are hoping SEO will save your business.
- You’re shopping for the cheapest price, tire-kicking, or not a US-based brand. (We only work with US brands.)
Common Questions