What’s The Difference Between 404 Error And 410 SEO?
The primary difference between 404 and 410 errors lies in their permanence and SEO impact. A 404 error indicates content is temporarily unavailable and might return later. A 410 error signals permanent content deletion and instructs search engines to remove URLs completely.
HTTP status codes are three-digit server responses that communicate page availability to browsers and search engines. At Eclipse Marketing, we’ve helped countless businesses optimize their technical SEO through proper status code implementation. These codes directly affect your website’s crawlability, indexing, and search rankings. Understanding their differences helps you manage your site’s technical SEO effectively.
404 errors tell search engines to keep checking back for content restoration. 410 errors instruct crawlers to stop indexing and remove pages permanently. Using the correct status code prevents crawl budget waste and maintains clean search indexes.
This comprehensive guide covers essential HTTP status codes including 200, 301, 302, 304, 307, 403, 404, 410, 451, 500, and 503. You’ll learn when to use each code and how they impact your SEO performance.
What Are HTTP Status Codes and When Do You See Them?
HTTP status codes are three-digit messages servers send when browsers make requests. The server tells the browser whether it can fulfill the request or not. The official W3C specifications include dozens of status codes that most people rarely encounter. You can find a complete overview of status codes at HTTPstatuses.com.
Understanding how browsers retrieve web pages helps explain these codes better. Every website visit begins when you type a URL or search term. Your browser requests the site’s IP address for the specific web page. The server responds with a status code in the HTTP header. This code tells your browser what happened with the request.
When everything works correctly, the server sends an HTTP 200 code with the website content. However, problems can occur with the requested content or server. A missing page triggers a 404 error response from the server. Technical server issues result in a 500 Internal Server Error message.
HTTP status codes serve as vital tools for checking website and server health. Sites that regularly send incorrect HTTP codes to search engines face potential ranking problems. These improper codes can seriously damage your SEO performance over time.
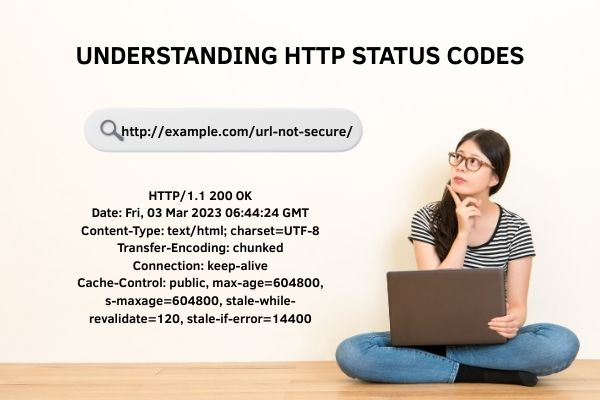
Here’s an example HTTP header showing a successful 200 OK response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Fri, 03 Mar 2023 06:44:24 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: public, max-age=604800, s-maxage=604800, stale-while-revalidate=120, stale-if-error=14400
Understanding the Five HTTP Status Code Categories
HTTP status codes fall into five distinct ranges that define different transaction aspects. Each range between client and server serves a specific communication purpose. Here are the five ranges and their main functions:
1xx – Information Codes 2xx – Success Codes 3xx – Redirect Codes 4xx – Client Error Codes 5xx – Server Error Codes
Fun fact: If you try brewing coffee in a teapot, you’ll get status code 418: I’m a teapot!

Essential HTTP Status Codes Every SEO Professional Should Know
The complete list of HTTP status codes is extensive and detailed. However, only a handful of these codes significantly impact your SEO efforts. Whether you’re managing your own website or working as an SEO professional, these codes deserve your attention. Our web design services include proper status code implementation to ensure optimal site performance. Let’s explore the most crucial status codes you’ll encounter regularly.
200: Page Found and Successfully Delivered
This represents the ideal scenario for any website interaction. A visitor requests content from your server, and the server responds perfectly. It sends back a 200 success message along with the requested content. Everyone wins in this situation: the server, the client, and most importantly, your visitor.
All status codes in the 2xx range indicate some form of successful communication. These codes tell search engines that your website is functioning properly and delivering content as expected.
301: Page Moved to New Location Forever
A 301 HTTP header appears when a requested URL has permanently moved to a different location. You’ll use this code frequently when managing your website’s structure and content organization. Creating 301 redirects helps you guide visitors from old URLs to new ones seamlessly.
Without proper 301 redirects, users encounter frustrating 404 error pages when accessing outdated links. This creates a poor user experience that you want to avoid at all costs. Implementing 301 redirects ensures that the SEO value from your old URL transfers completely to your new URL location. Professional Google consulting can help you implement these redirects correctly.
302: Page Temporarily Moved Elsewhere
A 302 status code means the requested content exists but lives at a different location temporarily. This code creates confusion because it doesn’t clearly indicate whether the move is temporary or permanent. Use 302 redirects only when you plan to temporarily redirect a URL and definitely return to using the original URL later.
Search engines understand that you intend to reuse the original URL eventually. Therefore, no SEO link value transfers to the new temporary location during a 302 redirect. Avoid using 302 redirects for permanent changes like domain moves or major site restructuring projects.
When you leave 302 redirects active for extended periods, search engines may interpret them as permanent 301 redirects. This can cause unintended SEO consequences that hurt your search rankings over time.
304: Content Unchanged Since Last Visit
A 304 status code tells browsers that the requested content hasn’t changed since their last visit. The server doesn’t need to send the same content again unnecessarily. Instead, it instructs the browser to use the cached version it already stored locally.
This response code helps save valuable crawl budget for larger websites with extensive content. Google’s crawlers skip unchanged pages and focus their attention on new or updated content instead. This efficient system helps search engines discover your fresh content more quickly and effectively. Google’s official documentation provides detailed information about crawl budget optimization.
307: True Temporary Redirect with Method Preservation
The 307 status code replaced the 302 redirect in HTTP1.1 protocol versions. Many consider it the only genuine temporary redirect option available today. Use 307 redirects when you need temporary URL changes while preserving the original request method completely.
A 307 redirect functions similarly to a 302 but provides clearer communication about temporary status. It explicitly tells browsers and search engines that the URL has a temporary new location. The redirect situation may change over time, so clients must continue using the original URL for future requests.
403: Access Denied to This Content
A 403 status code informs browsers that the requested content is completely forbidden for that user. The content remains inaccessible unless the visitor provides correct login credentials or proper authorization. This restriction stays in place until the user gains appropriate access permissions.
404: Page Cannot Be Found Anywhere
The 404 status code ranks among the most visible and important HTTP codes. When servers return 404 errors, the requested content simply doesn’t exist or has been deleted. Avoid frustrating your visitors with these error messages by fixing them promptly when possible.
Create redirects to send users from broken URLs to relevant new content or related pages. This approach maintains a positive user experience while preserving your site’s navigation flow.
Monitor 404 errors regularly through Google Search Console and minimize their occurrence across your website. Excessive 404 errors signal poor website maintenance to Google’s algorithms. This negative signal can potentially damage your overall search rankings over time.
When pages are intentionally removed and should disappear permanently, use 410 status codes instead. This sends a clearer signal to Google about your content management intentions. Our Denver SEO agency specializes in helping businesses manage these technical SEO elements effectively.
410: Content Permanently Deleted from Website
A 410 status code produces the same user result as a 404 error. However, 410 codes specifically tell search engines that you intentionally deleted the requested content. This makes it much more precise and informative than generic 404 messages.
Using a 410 essentially instructs search engines to remove the URL from their index completely. Before permanently deleting content from your website, consider whether equivalent pages exist elsewhere on your site.
If similar content exists, create a redirect to guide users to the relevant replacement page. If no equivalent exists, consider improving the existing content instead of deleting it entirely. The Moz Blog offers comprehensive guides on content optimization strategies.
451: Content Removed Due to Legal Requirements
The 451 status code indicates that requested content was removed for specific legal reasons. Use this code when you receive takedown requests or court orders requiring content removal. This status code clearly communicates to search engines why the page disappeared from your website.
500: Server Encountered Unexpected Problem
A 500 error delivers a generic message indicating your server hit an unexpected condition. The server couldn’t fulfill the visitor’s request without identifying the specific cause of the problem. These errors can originate from multiple sources across your website infrastructure.
Your web hosting provider might be experiencing technical difficulties or maintenance issues. Alternatively, a malfunctioning script on your website could trigger these server errors. Check your server’s error logs to identify exactly where things went wrong and fix the underlying issue. Web.dev provides excellent resources for debugging server-side issues.
503: Server Temporarily Cannot Handle Requests
A 503 status code represents a server-side error indicating temporary inability to handle requests. This typically occurs due to server overloading, scheduled maintenance, or other temporary technical issues. The server expects to resolve these problems within a reasonable timeframe.
Extended 503 errors can negatively impact your SEO performance over time. Search engines may interpret persistent unavailability as site unreliability or poor maintenance practices. This perception can hurt your search rankings if the situation continues too long.
Use 503 status codes only for genuine short-term situations with clear resolution timelines. Provide search engine crawlers with specific information about when your site will return online. Implement the Retry-After header value to instruct crawlers when they should attempt accessing your site again.
How to Use 404 and 410 Status Codes Effectively
Using 404 Not Found Status Codes Correctly
- When to Use 404 Codes: Apply 404 codes when pages are temporarily unavailable or might return later. This tells search engines to check back for the content eventually.
- Create Better 404 Error Pages: Design helpful 404 pages that include links to relevant content and popular sections. This approach significantly improves user experience when visitors encounter broken links. Our marketing services include custom 404 page design and optimization.
- Monitor and Fix Broken Links: Check for 404 errors regularly using tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Google Search Console. Fix broken links or create redirects to maintain your site’s health.
Example: A blog post temporarily removed for major revisions should return a 404 status code.
Using 410 Gone Status Codes Strategically
- When to Use 410 Codes: Apply 410 codes when pages are permanently deleted and will never return to your website. This provides clear, definitive information to search engines about content removal.
- Help Search Engines Clean Their Index: This status code helps search engines quickly remove the page from their index. This keeps search results clean and accurate for users. SEMrush’s blog offers detailed insights into index management strategies.
- Track Your Changes: Keep detailed logs of all 410 status changes for future reference and troubleshooting purposes.
Example: A product page for permanently discontinued items should return a 410 status code.
Following these practices ensures clear communication with search engines while maintaining an efficient, user-friendly website experience. Our Las Vegas SEO services help businesses implement these technical optimizations for improved search performance.
Conclusion
Understanding HTTP status codes transforms how you manage your website’s SEO performance and user experience. These three-digit messages directly influence how search engines crawl, index, and rank your content.
Implement proper redirects using 301 codes for permanent moves and 302 or 307 for temporary changes. Monitor 404 errors regularly and fix them promptly to maintain visitor satisfaction. Use 410 codes strategically when content is permanently removed to help search engines clean their indexes efficiently.
Regular monitoring through Google Search Console helps you catch issues before they impact rankings. Create custom 404 pages that guide users to relevant content instead of dead ends.
Master these status codes to improve your website’s technical SEO foundation. Your search rankings and user experience will benefit from this proactive approach to website maintenance and optimization. Need professional help? Contact us to discuss your technical SEO requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main difference between 404 and 410 status codes?
A 404 error indicates content cannot be found but might return later. A 410 explicitly tells search engines content was permanently deleted. Use 404 for temporary removal and 410 for permanent deletion decisions.
When should I use 301 redirects instead of 302 redirects?
Use 301 redirects for permanent content moves, transferring all SEO value to new URLs. Choose 302 redirects only for temporary moves where you’ll restore original URLs. Always use 301 for domain migrations and permanent changes.
Do too many 404 errors hurt my SEO rankings?
Excessive 404 errors can negatively impact SEO performance over time. Search engines interpret numerous broken links as poor maintenance. However, occasional 404 errors won’t immediately destroy rankings if addressed promptly through Google Search Console.
How do I create an effective 404 error page?
Design 404 pages that help users find relevant content instead of leaving. Include homepage links, popular sections, and search functionality. Use clear, friendly language without technical jargon and add recent posts or navigation to keep users engaged.
What’s the difference between 500 and 503 server errors?
A 500 error indicates unexpected server conditions requiring log investigation. A 503 means temporary unavailability due to maintenance or overloading. Use 503 codes during planned maintenance with Retry-After headers for search engines.

Mike has over 5 years of experience helping clients improve their business visibility on Google. He combines his love for teaching with his entrepreneurial spirit to develop innovative marketing strategies. Inspired by the big AI wave of 2023, Mike now focuses on staying updated with the latest AI tools and techniques. He is committed to using these advancements to deliver great results for his clients, keeping them ahead in the competitive online market.